Search
Praetorian prefecture of the East

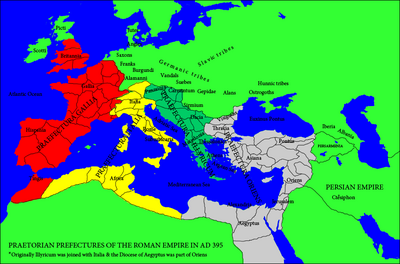
The praetorian prefecture of the East, or of the Orient (Latin: praefectura praetorio Orientis, Greek: ἐπαρχότης/ὑπαρχία τῶν πραιτωρίων τῆς ἀνατολῆς) was one of four large praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided. As it comprised the larger part of the Eastern Roman Empire, and its seat was at Constantinople, the praetorian prefect was the second most powerful man in the East, after the Emperor, in essence serving as his first minister.
Structure
The Prefecture was established after the death of Constantine the Great in 337, when the empire was split up among his sons and Constantius II received the rule of the East, with a praetorian prefect as his chief aide. The part allotted to Constantius encompassed four (later five) dioceses, each in turn comprising several provinces. The authority of the prefecture stretched from the Eastern Balkans, grouped into the Diocese of Thrace, to Asia Minor, divided into the dioceses of Asiana and Pontus, and the Middle East, with the dioceses of Orient and Egypt.
List of known praefecti praetorio Orientis
- Pompeius Probus
- Ablabius (329-337/338)
- Septimius Acindynus (338–340)
- Philippus (344–351)
- Thalassius (351 - 354)
- Domitianus (354)
- Strategius Musonianus (354–358)
- Flavius Hermogenes (358-360)
- Helpidius (360)
- Saturninius Secundus Salutius (361 until some years into the reign of Valentinian)
- Nebridius
- Domitius Modestus (369–377)
- Quintus Clodius Hermogenianus Olybrius (379)
- Neoterius (380-381)
- Maternus Cynegius (384–388)
- Eutolmius Tatianus (388–392)
- Flavius Rufinus (392, September 10 – 395, November 27)
- Caesarius (1st time, 395, November 30 – 397, July 13)
- Eutychianus (1st time, 397, September 4 – 399, July 25)
- Aurelianus (1st time, 399, August 17 – October 2)
- possibly Eutychianus (2nd time, 399, December 11 – 400, July 12)
- Caesarius (2nd time, 400–403)
- Eutychianus (3rd time, 404–405)
- Flavius Anthemius (405–414)
- Monaxius (1st time, 10 May – 30 November 414)
- Aurelianus (2nd time, 414–416)
- Monaxius (2nd time, 26 August 416 – 27 May 420)
- Eustathius (420–422)
- Asclepiodotus (423–425)
- Aetius (425)
- Hierius (1st time, 425–428)
- Flavius Florentius (1st time, 428–430)
- Antiochus Chuzon (430–431)
- Rufinus (431–432)
- Hierius (2nd time, 432)
- Flavius Taurus (1st time, 433–434)
- Anthemius Isidorus (435–436)
- Darius (436–437)
- Flavius Florentius (2nd time, c. 438–439)
- Flavius Taurus Seleucus Cyrus (439–441)
- Thomas (442)
- Apollonius (442–443)
- Zoilus (444)
- Hermocrates (444)
- Flavius Taurus (2nd time, 445)
- Flavius Constantinus (first term, c. 447)
- Antiochus (448)
- Flavius Florentius Romanus Protogenes (448–449)
- Hormisdas (449–450)
- Palladius (450–455)
- Flavius Constantinus (second term, 456)
- Flavius Constantinus (third term, 459)
- Flavius Antoninus Messala Vivianus (459–460)
- Pusaeus (465)
- Amasius (c. 469)
- Matronianus (491)
- Hierius (494–496)
- Euphemius (496)
- Polycarpus (498)
- Constantine (1st time, 502)
- Appion (503)
- Leontius (503–504)
- Constantine (2nd time, 505)
- Eustathius (505–506)
- Zoticus (511–512)
- Marinus (1st time, c. 512–515)
- Sergius (517)
- Marinus (2nd time, 519)
- Demosthenes (520–524)
- Archelaus (524–527)
- Basilides (c. 527)
- Atarbius (c. 528)
- Iulianus (530–531)
- John the Cappadocian (1st time, 531–532)
- Phokas (533)
- John the Cappadocian (2nd time, 533–541)
- Flavius Comitas Theodorus Bassus (c. 541) as John's deputy
- Peter Barsymes (1st time, 543–546)
- Flavius Comitas Theodorus Bassus (c. 548)
- Addaeus (c. 551)
- Hephaestus (551–552)
- Areobindus (c. 553)
- Peter Barsymes (2nd time, 555–562)
- Diomedes (c. 572)
- Georgius (c. 598)
- Constantine Lardys (c. 602)
References
Sources
- The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire (PLRE), Vols. I-III: (Vol. II, pp. 1250–1252;)
- Palme, Bernhard (2007). "The Imperial Presence: Government and Army". Egypt in the Byzantine World, 300-700. Cambridge University Press. pp. 244–270. ISBN 9780521871372.
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: Praetorian prefecture of the East by Wikipedia (Historical)
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou


