Search
Respiratory bronchiolitis

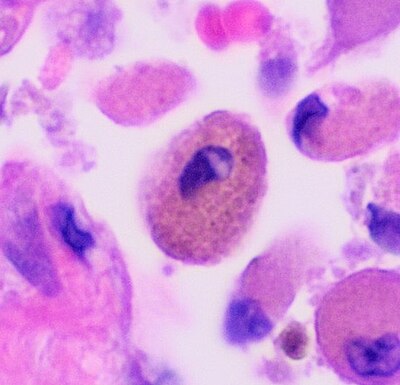
Respiratory bronchiolitis is a lung disease associated with tobacco smoking. In pathology, it is defined by the presence of "smoker's macrophages". When manifesting significant clinical symptoms it is referred to as respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD).
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of respiratory bronchiolitis requires a correlation of clinical, radiologic and pathologic findings:
- Clinical: Symptoms and pulmonary function testing
- Radiologic: Chest radiograph and high-resolution computed tomography
- Pathologic: Lung biopsy with "smoker's macrophages" limited to distal airspaces and peribronchiolar airspaces, and minimal to absent peribronchiolar interstitial fibrotic thickening
Respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease
Respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease is respiratory bronchiolitis that manifests as a clinically significant interstitial lung disease. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia associated with smoking.
It is a histological finding, not a pathological description. When associated with disease, it is known as "Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease" or "RB-ILD". Also, this disease is predominantly found in the upper lobe with centrilobar ground glass nodules. Importantly, no fibrosis is involved, just bronchial wall thickening. Treatment is to stop smoking.
The appearance is similar to desquamative interstitial pneumonia, and some have suggested that the two conditions are caused by the same processes.
See also
- Bronchiolitis
References
External links
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: Respiratory bronchiolitis by Wikipedia (Historical)
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou



