Search
Maybach VL II

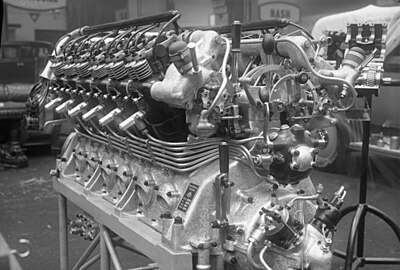
The Maybach VL II was a type of internal combustion engine built by the German company Maybach in the late 1920s and 1930s. It was an uprated development of the successful Maybach VL I, and like the VL I, was a 60° V-12 engine.
History
Five of them powered the German airship Graf Zeppelin, housed in separate nacelles. The engines developed 410 kW (550 hp) and were of 33.251 L (2,029.1 cu in) capacity. They could burn either Blau gas or petrol. The American USS Akron used eight of them, mounted internally, as did its sister ship Macon. The engines were reversible, meaning different cams could be engaged allowing the engine crankshaft to run in either direction, enabling reverse thrust.
Lürssen built the fast yacht Oheka II in 1927; powered by three VL IIs, it was the fastest vessel of its type and became the basis of Germany's E-boats of World War II.
Applications
- LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin
- USS Akron (ZRS-4)
- USS Macon (ZRS-5)
- Oheka II
Specifications
Data from National Air and Space Museum
General characteristics
- Type: V-12 four-stroke liquid-cooled piston engine
- Bore: 140 mm (5.5 in)
- Stroke: 180 mm (7.1 in)
- Displacement: 33,300 cm3 (2,030 cu in)
- Length: 195.6 cm (77.0 in)
- Width: 91.4 cm (36.0 in)
- Height: 96.5 cm (38.0 in)
- Dry weight: 809.2 kg (1,784 lb)
Components
- Cooling system: Liquid-cooled
Performance
- Power output: 430 kW (570 hp) at 1,600 rpm
See also
Related development
- Maybach VL I
Related lists
- List of aircraft engines
References
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: Maybach VL II by Wikipedia (Historical)
Articles connexes
- Maybach VL I
- Oheka II
- USS Akron
- USS Macon (ZRS-5)
- LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin
- Allison V-1710
- List of aircraft engines
- Zeppelin Museum Friedrichshafen
- Sd.Kfz. 9
- USS Los Angeles (ZR-3)
- List of military equipment of Germany's allies on the Eastern front
- Hummel (vehicle)
- Sturmgeschütz III
- Panzer IV
- Lvkv m/43
- Big Three (automobile manufacturers)
- List of 2021 albums (July–December)
- Madrid, Zaragoza and Alicante railway
- 2018 in hip hop music
- 2020 in hip hop music
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou



