Search
Phenyl glycidyl ether

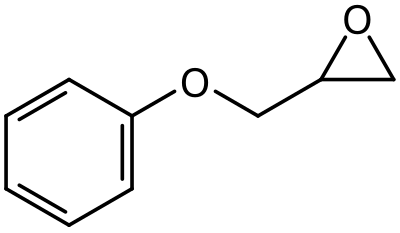
Phenyl glycidyl ether, is a liquid aromatic organic chemical in the glycidyl ether class of compounds. It has the formula C9H10O2. It has the CAS Registry Number 122-60-1 and the IUPAC name of 2-(phenoxymethyl)oxirane. A key use is in the viscosity reduction of epoxy resin systems. It is REACH registered and on EINECS under the name 2,3-epoxypropyl phenyl ether.
Manufacture
Phenol and epichlorohydrin are reacted in the presence of a base and not a Lewis acid catalyst as normal with glycidyl ethers. A halohydrin is formed. This is followed by washing with sodium hydroxide in dehydrochlorination step. This forms phenyl glycidyl ether. The waste products are water and sodium chloride and excess caustic soda. One of the quality control tests would involve measuring the Epoxy value by determination of the epoxy equivalent weight.
Other names
- phenyl glycidyl ether
- phenol glycidyl ether
- 1,2-Epoxy-3-phenoxypropane
- 1-Phenoxy-2,3-epoxypropane
- 2,3-Epoxy-1-phenoxypropane
- 2,3-Epoxypropyl phenyl ether
- 3-phenoxy-1,2-epoxypropane
- benzene, (2,3-epoxypropoxy)-
- Ether, 2,3-epoxypropyl phenyl
- Glycidyl phenyl ether
- Oxirane, (phenoxymethyl)-
- propane, 1,2-epoxy-3-phenoxy-
Uses
It has been used for carbon dioxide absorption and other chemical reactions in addition to its use of reducing viscosity of epoxy resins. It undergoes anionic polymerization. It is one of a number of glycidyl ethers available commercially that are used to reduce the viscosity of epoxy resins. These are then further used in coatings, sealants, adhesives and elastomers. The use of the diluent does effect mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins.
Toxicology
It has caused cancer in laboratory animals. It is also listed as a California Proposition 65 chemical. It is specifically mentioned by OSHA.
See also
- Epoxide
- Glycidol
References
Further reading
- Epoxy resin technology. Paul F. Bruins, Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn. New York: Interscience Publishers. 1968. ISBN 0-470-11390-1. OCLC 182890.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - Flick, Ernest W. (1993). Epoxy resins, curing agents, compounds, and modifiers : an industrial guide. Park Ridge, NJ. ISBN 978-0-8155-1708-5. OCLC 915134542.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lee, Henry (1967). Handbook of epoxy resins. Kris Neville ([2nd, expanded work] ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-036997-6. OCLC 311631322.
- "Dow Epoxy Resins" (PDF).
External links
- Safety Data Sheet
- Phenyl glycidyl ether supplier distributor parchem
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: Phenyl glycidyl ether by Wikipedia (Historical)
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou