Search
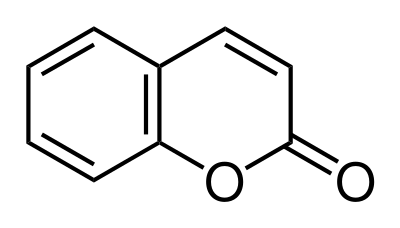
Coumarin derivatives

Coumarin derivatives are derivatives of coumarin and are considered phenylpropanoids. Among the most important derivatives are the 4-hydroxycoumarins, which exhibit anticoagulant properties, a characteristic not present for coumarin itself.
Some naturally occurring coumarin derivatives include umbelliferone (7-hydroxycoumarin), aesculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin), herniarin (7-methoxycoumarin), psoralen and imperatorin.
4-Phenylcoumarin is the backbone of the neoflavones, a type of neoflavonoids.
Coumarin pyrazole hybrids have been synthesized from hydrazones, carbazones and thiocarbazones via Vilsmeier Haack formylation reaction.
Compounds derived from coumarin are also called coumarins or coumarinoids; this family includes:
- brodifacoum
- bromadiolone
- difenacoum
- auraptene
- ensaculin
- phenprocoumon (Marcoumar)
- PSB-SB-487
- PSB-SB-1202
- scopoletin can be isolated from the bark of Shorea pinanga
- warfarin (Coumadin)
Coumarin is transformed into the natural anticoagulant dicoumarol by a number of species of fungi. This occurs as the result of the production of 4-hydroxycoumarin, then further (in the presence of naturally occurring formaldehyde) into the actual anticoagulant dicoumarol, a fermentation product and mycotoxin. Dicoumarol was responsible for the bleeding disease known historically as "sweet clover disease" in cattle eating moldy sweet clover silage. In basic research, preliminary evidence exists for coumarin having various biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antibacterial, and antifungal properties, among others.
Uses
Medicine
Warfarin – a coumarin – with brand name, Coumadin, is a prescription drug used as an anticoagulant to inhibit formation of blood clots, and so is a therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It may be used to prevent recurrent blood clot formation from atrial fibrillation, thrombotic stroke, and transient ischemic attacks.
Coumarins have shown some evidence of biological activity and have limited approval for few medical uses as pharmaceuticals, such as in the treatment of lymphedema. Both coumarin and 1,3-indandione derivatives produce a uricosuric effect, presumably by interfering with the renal tubular reabsorption of urate.
Laser dyes
Coumarin dyes are extensively used as gain media in blue-green tunable organic dye lasers. Among the various coumarin laser dyes are coumarins 480, 490, 504, 521, 504T, and 521T. Coumarin tetramethyl laser dyes offer wide tunability and high laser gain, and they are also used as active medium in coherent OLED emitters. and as a sensitizer in older photovoltaic technologies.
References
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: Coumarin derivatives by Wikipedia (Historical)
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou