Search
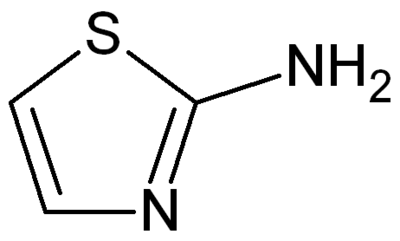
2-Aminothiazole

2-Aminothiazole is a heterocyclic amine featuring a thiazole core. It can also be considered a cyclic isothiourea. It possesses an odor similar to pyridine and is soluble in water, alcohols and diethyl ether. 2-Aminothiazole itself is mainly of academic interest, with few exceptions. It is a precursor to a sulfathiazole ("sulfa drugs"). 2-Aminothiazole can be used as a thyroid inhibitor in the treatment of hyperthyroidism.
2-Aminothiazole is prepared from paraldehyde, thiourea, and sulfuryl chloride.
2-Aminothiazoles
Like the parent, 2-aminothiazoles are often produced by the condensation of thiourea and an alpha-halo ketone.
In an adaptation of the Robinson-Gabriel synthesis, a 2-acylamino-ketone reacts with phosphorus pentasulfide.
Applications
Synthetic aminothiazoles - compounds containing the parent 2-aminothiazole as a subunit - are used in medicinal chemistry. Some examples are abafungin, acotiamide, amiphenazole, amthamine, avatrombopag, aztreonam, cefepime, cefixime, ceftizoxime, ceftiofur, ceftibuten, cefpirome, famotidine, meloxicam, and pramipexole.
References
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: 2-Aminothiazole by Wikipedia (Historical)
Articles connexes
- 2-Aminooxazole
- Cyanamide
- Thiazole
- Α-Halo ketone
- C3H4N2S
- Glossary of chemical formulae
- Cefepime
- Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase III
- Cefdinir
- 2-Imidazolidinethione
- Cook–Heilbron thiazole synthesis
- Discovery and development of cephalosporins
- Chloroacetaldehyde
- Ritanserin
- Thiourea
- Cefditoren
- Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
- Cdc25
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou

